-
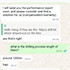 RitaThe tricone bit quality is good
RitaThe tricone bit quality is good -
 Guramyour bit retrived from the hole ,just let you i am pressed , it performed well .And retrieved bit is like new .
Guramyour bit retrived from the hole ,just let you i am pressed , it performed well .And retrieved bit is like new .
TCI Tricone Bit 9-7/8 Inch IADC 645 of API Drilling Tools
| Machine Type | Drilling Tool | Certification | API |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Name | Tricone Drill Bit | Market | All Over The Word |
| Highlight | IADC Code 645 Tricone Drill Bit,9 7/8 Inch Tricone Drill Bit,Tricone Rock Drill Tool |
||
Description :
A tricone bit is a mechanical drill bit located in the bottom hole assembly. The bit cuts away the surface of the rock being drilled through rotation and mechanical friction caused by the teeth of the bit. Tricone bits are designed to take the energy of the rotating drill string and the supply of mud and to apply this force to deepen the well.
How the know a tricone Bit quality ?
- Tricon Bit IADC code passport
- Tricone Bit of TCI & Steel tooth options
- Tricone Bit Additional tungsten carbide inserts on heel rows
- Tricone Bit Tungsten carbide coating on cone bodies
- Tricone Bit Diamond coated tungsten carbide inserts on the gauge of the cones
- Tricone Bit Tungsten carbide inserts on the shirttail of the legs
- Tricone Bit Additional central nozzle for cleaning cones
The tricone Bit feature is that they come with their own passport as below :
- The specification of the cones
- The quality stamp signed by the person who made and checked the bit
- The recommended drilling parameters to get the best performance out of the bit:
- Bit weight
- Rotation speed
- Flushing volume
Applications
- Geotechnical investigation
- Mining exploration & Probing
- Geotechnical instrumentation
- Geophysics
Which type of tricone bit you choose depends on the geology you are drilling in and the diameters of the borehole you are drilling. The International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC) have developed an easy use step system to choose the right tricone for your geology with additional features such as bit protection for longer production life.
| Tungsten carbide Inserts | ||
| Form | Performance | Application |
| Chisel | High Penetration for Plastic Rock | Plastic Rock soft& Medium Hard |
| Conical | Same as chisel plus high breaking and Rotation Resistance | Fragile Rocks medium to hard |
| Ball | Very High Breaking Resistance | Fragile Rocks medium to hard |
Tricone Bearing Types
There are primarily three types of bearing designs used in tricone drilling bits:
• STANDARD OPEN BEARING ROLLER BIT:
On these bits the cones will spin freely. This type of bit has a front row of ball bearings and a back row of roller bearings.
• SEALED BEARING ROLLERS BITS
These bits have an O-Ring seal with a grease reservoir for bearing cooling. The seals acts as a barrier against mud and cuttings to protect the bearings
• JOURNAL BEARING ROLLER BITS
These bits are strictly oil/grease cooled with nose bearings, O-Ring seal and a race for maximum performance.
IADC Codes
IADC Codes make it easier to describe what kind of rock bit is required.
The first three digits classify the bit according to the formation it is designed to drill and the bearing/seal design used.
1, 2, and 3 designate STEEL TOOTH BITS with 1 for soft, 2 for medium and 3 for hard formations.
Codes 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 designate TUNGSTEN CARBIDE INSERT BITS for varying formation hardness with 4 being the softest and 8 the hardest
Formation Types:
The following shows the typical formation and its IADC reference
1 & 4 Soft formations with sticky layers and low compressive strength, such as clay, marls.
1 & 4 Soft formations with low compressive strength such as marl, salt, anhydrite and shale.
5 Soft to medium formations with low compressive strength and inter-bedded with hard layers, such as sands, shale and chalk.
2 or 6 Medium to hard dense formations with high to very high compressive strength, but with non-abrasive or small abrasive layers, such as shales, mudstone, sandstone, limestone, dolomite and anhydrite.
3 or 7 Hard and dense formations with very high compressive strength and some abrasive layers, such as siltstone, sandstone and mudstone.
8 Extremely hard and abrasive formations such as quartzite and volcanic rock.