-
 RitaThe tricone bit quality is good
RitaThe tricone bit quality is good -
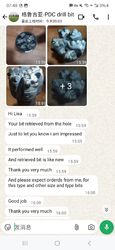 Guramyour bit retrived from the hole ,just let you i am pressed , it performed well .And retrieved bit is like new .
Guramyour bit retrived from the hole ,just let you i am pressed , it performed well .And retrieved bit is like new .
TCI 9-1/2" Tricone Drill Bit IADC 537 Of Rock Drilling
| Highlight | 9-1/2" TCI Tricone Bit,Oilfield Tricone Drill Bit,Drilling Tricone Bit |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Description
A tricone bit is an essential component of the bottom hole assembly used in drilling operations.
This mechanical drill bit utilizes rotational motion and the mechanical friction generated by its teeth to remove the rock surface during drilling.
Its purpose is to harness the energy from the rotating drill string and the mud supply, effectively applying this force to facilitate well deepening.
![]()
| Tungsten carbide Inserts | ||
| Form | Performance | Application |
| Chisel | High Penetration for Plastic Rock | Plastic Rock soft& Medium Hard |
| Conical | Same as chisel plus high breaking and Rotation Resistance | Fragile Rocks medium to hard |
| Ball | Very High Breaking Resistance | Fragile Rocks medium to hard |
Bearing Types
• STANDARD OPEN BEARING ROLLER BIT
On these bits the cones will spin freely. This type of bit has a front row of ball bearings and a back row of roller bearings.
• SEALED BEARING ROLLERS BITS
These bits have an O-Ring seal with a grease reservoir for bearing cooling. The seals acts as a barrier against mud and cuttings to protect the bearings.
• JOURNAL BEARING ROLLER BITS
These bits are strictly oil/grease cooled with nose bearings, O-Ring seal and a race for maximum performance.
Formation Types
1 & 4 Soft formations with sticky layers and low compressive strength, such as clay, marls.
1 & 4 Soft formations with low compressive strength such as marl, salt, anhydrite and shale.
5 Soft to medium formations with low compressive strength and inter-bedded with hard layers, such as sands, shale and chalk.
2 or 6 Medium to hard dense formations with high to very high compressive strength, but with non-abrasive or small abrasive layers, such as shales, mudstone, sandstone, limestone, dolomite and anhydrite.
3 or 7 Hard and dense formations with very high compressive strength and some abrasive layers, such as siltstone, sandstone and mudstone.
8 Extremely hard and abrasive formations such as quartzite and volcanic rock.